Before I proceed, you should know that Ubuntu always comes with a GNOME flavor and you can download and install the complete OS from GetUbuntuGNOME page.
Now, if you have installed the usual Ubuntu 16.04 LTS with Unity desktop interface and want to install GNOME in your Ubuntu system, this article will demonstrate you the steps.
It's been a while for the launch of Ubuntu 16.04 LTS Xenial Xerus and the installation process for GNOME is not that hard. GNOME 3 comes with a nice user interface with an easy to use design and comes with various features.
Lets see how we can install GNOME 3 in our Ubuntu 16.04.
Open terminal through Ubuntu Dash or by pressing Ctrl + Alt + T and type in the following command:
sudo apt-get install gnome-shell
This will ask you the root password and 100mb free disk space. Once confirmed, it will install the GNOME Shell. Note that GNOME shell and GNOME desktop are different and this will install the shell only with the user interface.
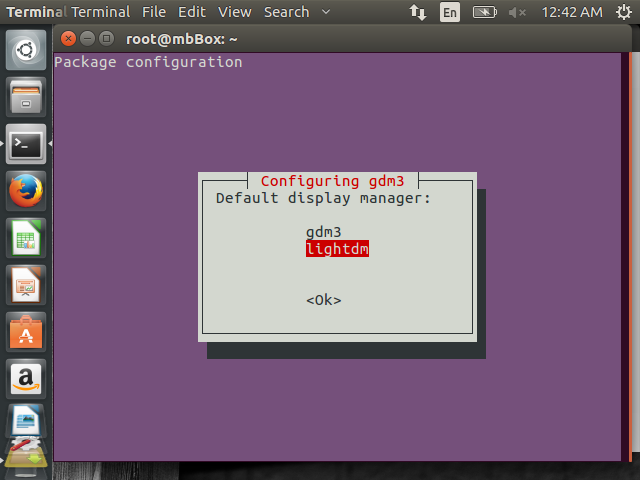
In the installation process, the package configuration will ask for gdm3 / lightdm. Select lightdm and press <OK>.
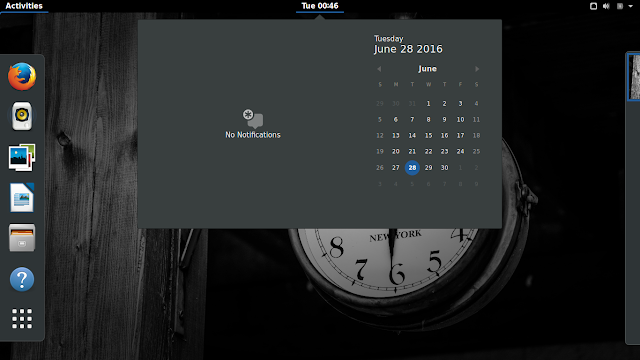
Once done, this will finish up the installation in some min. Log off your system and at the login screen switch to GNOME from Ubuntu.
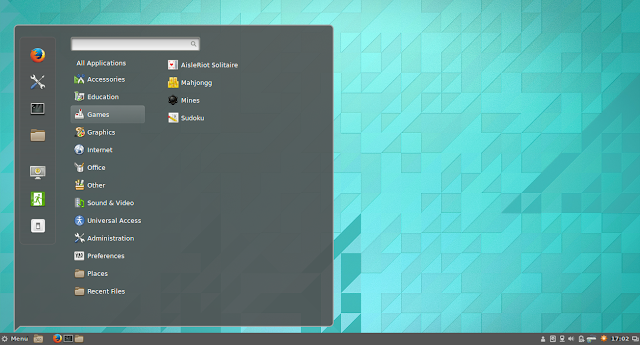
Once you login with your credentials in the GNOME shell, you will see the GNOME shell. Try it, use it and love it.
Now, in case you are not satisfied with GNOME in Ubuntu 16.04 and remove it, just type in the following command in the terminal.
sudo apt-get remove gnome-shell
Feels nice, isn't it? Tell us in the comments!